
When creating custom products, the quality of the artwork file is key to producing a stunning final result. Whether it's screen-printed labels, cotton labels, custom pins, or heat transfers, using the right file format—vector or raster—can greatly impact the clarity, scalability, and detail of the finished piece. Let’s break down the differences between these two formats and why understanding them is essential for custom product orders.
What is the Difference Between Raster and Vector Graphics?
Vector Graphics
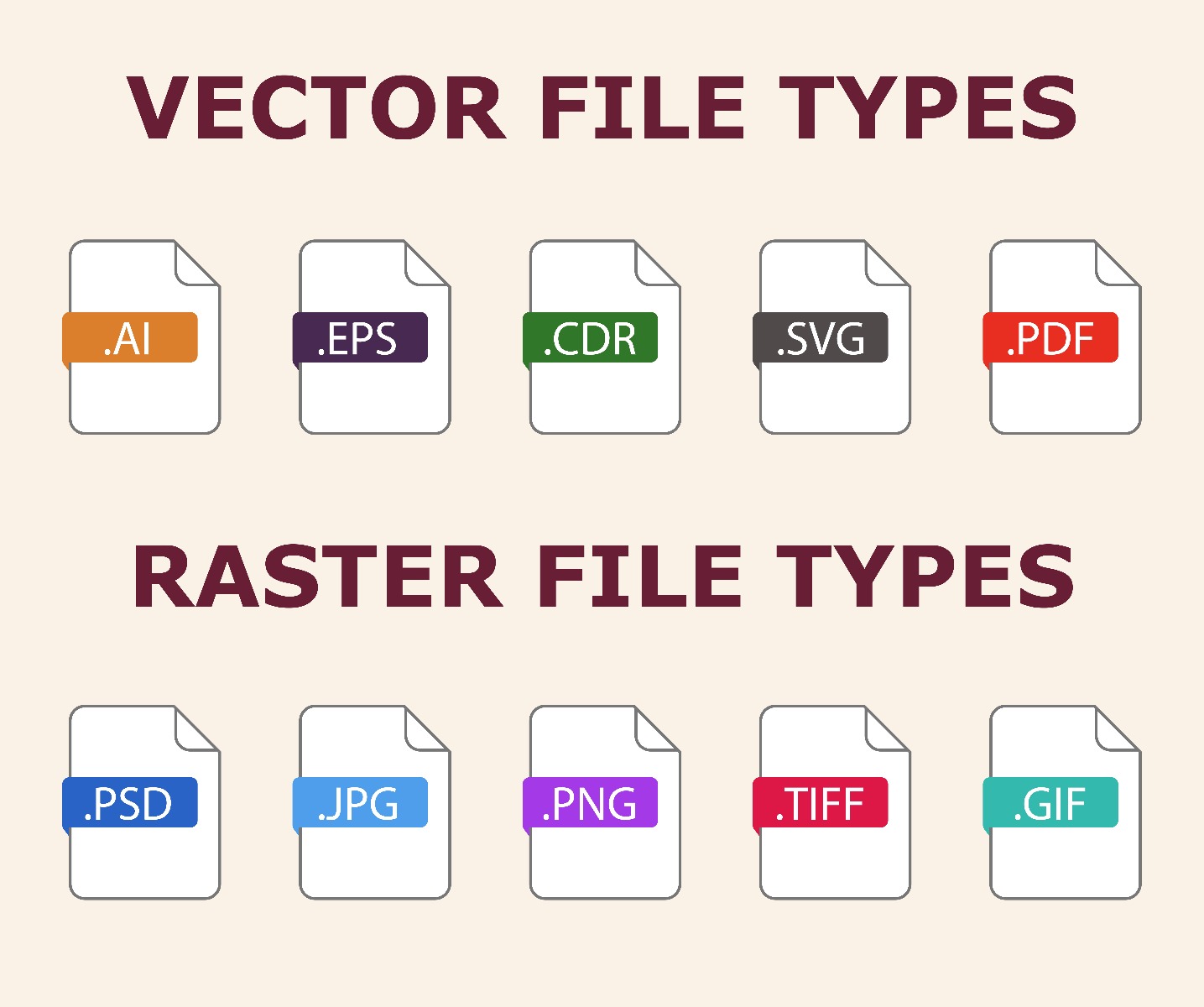
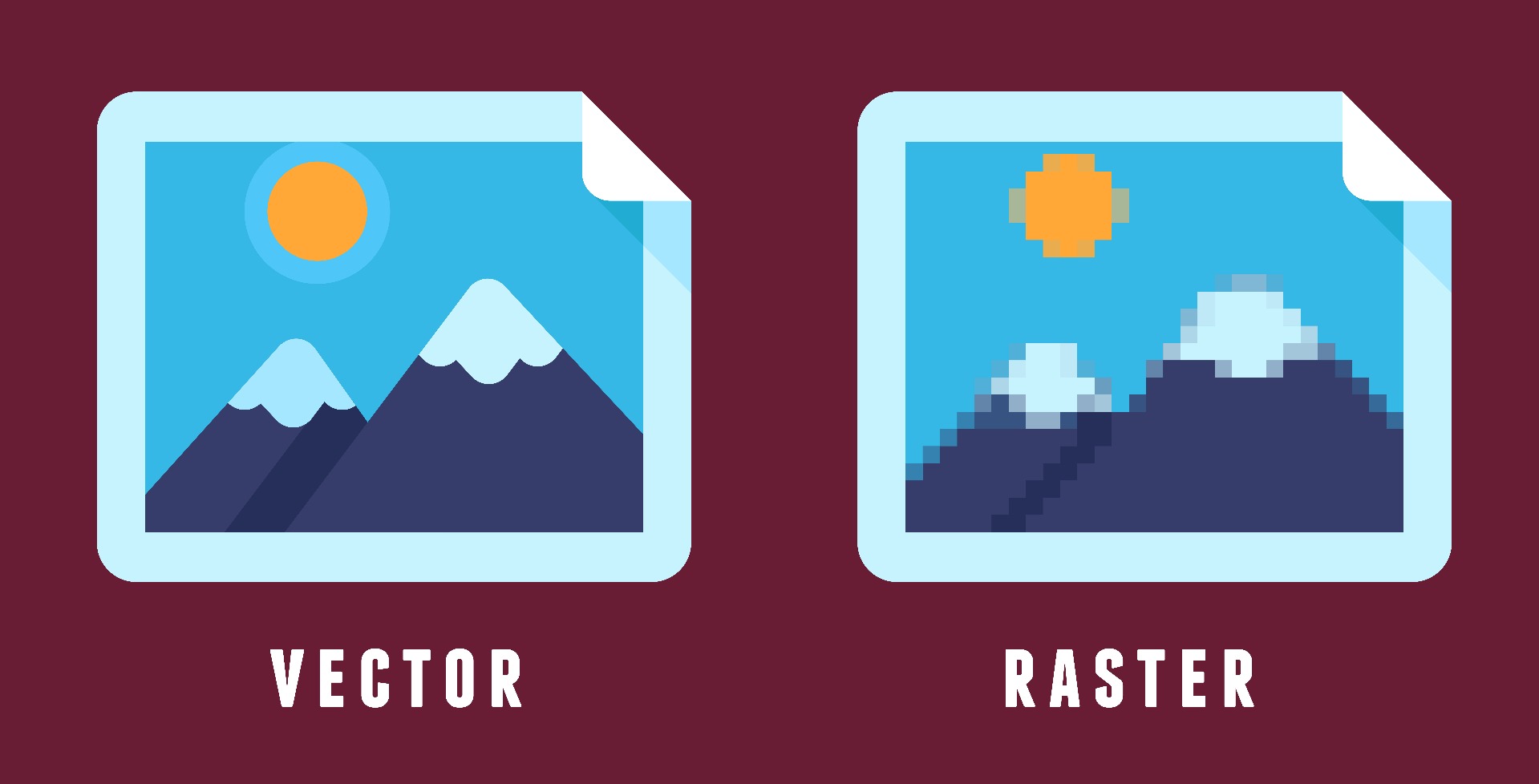
Vector graphics are made up of points, lines, and shapes defined by mathematical equations, rather than pixels. This structure allows them to be scaled up or down without losing clarity, making them ideal for designs that need to be resized frequently, such as logos or text-based artwork. Vector files are highly versatile, enabling smooth adjustments without any quality loss. Common file formats for vector graphics include AI (Adobe Illustrator), EPS, CDR (CorelDRAW), SVG and PDF.
Raster Graphics
Raster graphics are composed of pixels—tiny squares of color. This pixel-based structure is excellent for detailed, complex images such as photographs but has limitations when it comes to resizing. When a raster image is scaled up, it can become pixelated or blurry, as the individual pixels are simply enlarged. Raster files are commonly used in formats like JPEG, PNG, TIFF, and PSD (Adobe Photoshop).
Choosing the Right Format for Custom Products

Different products have different requirements when it comes to artwork files. Here’s a guide on which format works best for various custom products:
- Products Requiring Vector Artwork Only: For screen-printed labels, cotton labels, custom pins, heat transfers, hang tags, PVC patches, TPU labels, Tyvek labels, and printed care labels, vector files are essential. Vector artwork is necessary because it provides high scalability and sharp clarity, and the production processes for these products require vector file formats.
- Products Accepting Both Raster and Vector Files: Products like woven labels, woven patches, leather patches, embroidered patches, photo patches, chenille patches, sublimation printed labels, and woven ribbons can work with either raster or vector files. However, vector files are still preferred because they offer more flexibility and allow for easier adjustments if the design needs modification.
Why Vector Files Offer Greater Flexibility
Using a vector file provides significant advantages in the production process. Vector files are easier to edit, and individual elements in the design can be manipulated without affecting the overall quality. This means that if you or the manufacturer needs to make color changes, adjust the layout, or add text, vector files allow these modifications seamlessly. Raster files, on the other hand, may lose clarity with each edit, especially if the design requires resizing.
Recommended File Types for Custom Artworks
When submitting artwork for your custom products, it’s essential to use the correct file format to avoid potential issues in production. Here are the recommended formats:
- Vector Formats: AI (Adobe Illustrator), EPS, CDR (Corel Draw), SVG, PDF
- Raster Formats: PSD (Adobe Photoshop), PNG, JPG, TIFF, GIF
Understanding the difference between vector and raster files can make a significant difference in the outcome of your custom products. Using vector files whenever possible ensures high-quality results with maximum flexibility for adjustments. For products that require fine details or high-resolution photos, raster files can be used but may have limitations if resizing is needed. Choosing the correct file type helps your custom products look their best, meeting both your standards and those of your clients.




The information below is required for social login
Sign In
Create New Account